Exploring the World from Above: Mapping Ecosystems Using Drones
When we think about mapping ecosystems, the traditional image of scientists trekking through dense forests or wading through marshlands may come to mind. However, with the rapid advancements in technology, particularly in the field of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) or drones, mapping ecosystems has taken on a whole new dimension. Drones have revolutionized the way we study and understand our environment, offering unparalleled access to remote or challenging terrains. In this article, we will delve into the world of using drones to map ecosystems, exploring the methods, benefits, challenges, and future prospects of this innovative approach.
The Rise of Drones in Environmental Research

Over the past decade, drones have become increasingly popular in various fields, including environmental research and conservation. These small, unmanned aerial vehicles equipped with cameras, sensors, and GPS technology have opened up new avenues of exploration and data collection. When it comes to mapping ecosystems, drones offer several advantages over traditional methods. They can cover vast areas in a short amount of time, collect high-resolution imagery, and access hard-to-reach or hazardous locations with ease.
One of the key benefits of using drones for ecosystem mapping is the ability to create highly detailed and accurate maps. By capturing aerial images and data, researchers can analyze the landscape, vegetation, and biodiversity of an area with precision. This valuable information can help monitor changes over time, identify conservation priorities, and inform land management decisions.
The Process of Mapping Ecosystems Using Drones

The process of mapping ecosystems using drones involves several steps, from planning and data collection to analysis and interpretation. Here is an overview of the typical workflow:
1. Mission Planning
Before deploying a drone for ecosystem mapping, researchers need to carefully plan their mission. This involves defining the study area, setting flight parameters, selecting the appropriate drone and sensors, and obtaining any necessary permits or permissions. Mission planning is crucial to ensure the success and safety of the aerial survey.
2. Data Collection
Once the mission is planned, the drone is deployed to collect aerial imagery and other data. Drones can capture photos, videos, and other sensor data in high resolution, providing detailed information about the ecosystem. Researchers can customize the flight path, altitude, and camera settings to optimize data collection for their specific research goals.
3. Image Processing
After collecting the data, researchers need to process the images to create a map of the ecosystem. This involves stitching together the photos, georeferencing the images, and generating a digital terrain model. Software tools such as Pix4D, DroneDeploy, and Agisoft Metashape are commonly used for image processing and analysis.
4. Mapping and Analysis
Once the images are processed, researchers can start mapping and analyzing the ecosystem. By overlaying different layers of data, such as vegetation cover, land use, and topography, researchers can gain insights into the ecosystem’s structure and function. This information can help identify biodiversity hotspots, assess habitat quality, and monitor environmental changes over time.
Applications of Drone Mapping in Ecosystems

The use of drones for mapping ecosystems has a wide range of applications across various fields, including ecology, conservation, forestry, agriculture, and urban planning. Here are some key applications:
1. Habitat Monitoring
Drones can be used to monitor wildlife habitats, assess biodiversity, and track changes in vegetation cover. By conducting regular aerial surveys, researchers can identify habitat loss, fragmentation, and degradation, and implement targeted conservation measures to protect vulnerable species.
2. Forest Inventory
Forests are vital ecosystems that provide essential services such as carbon sequestration, water regulation, and biodiversity conservation. Drones can be used to conduct forest inventories, measure tree heights, estimate biomass, and monitor deforestation. This information is crucial for sustainable forest management and climate change mitigation efforts.
3. Wetland Mapping
Wetlands are diverse and productive ecosystems that play a critical role in flood control, water purification, and wildlife habitat. Drones can help map wetlands, monitor water quality, and assess wetland health. By identifying threats such as pollution, invasive species, and habitat loss, researchers can implement conservation strategies to protect these valuable ecosystems.
4. Agricultural Mapping
Agriculture is another field where drone mapping has found application. Drones can be used to monitor crop health, assess soil moisture levels, and optimize irrigation practices. By collecting real-time data on crop conditions, farmers can make informed decisions to improve crop yields, reduce inputs, and minimize environmental impact.
Challenges and Considerations
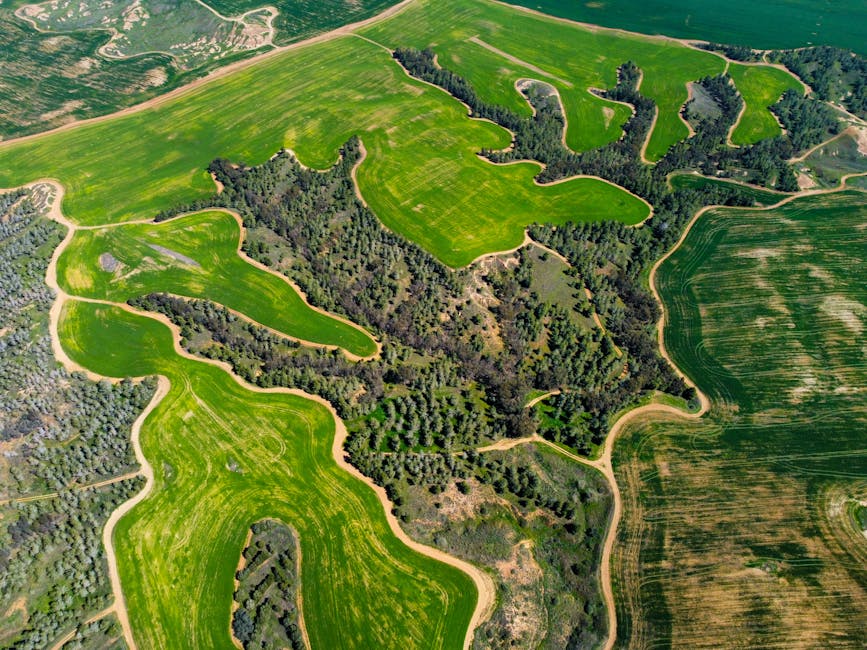

While drones offer many advantages for mapping ecosystems, there are also challenges and considerations that researchers need to address. Some of the key challenges include:
1. Data Processing
Processing and analyzing the large amounts of data collected by drones can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. Researchers need to have the necessary skills and tools to handle the data effectively and extract meaningful insights from the imagery.
2. Regulation and Compliance
Operating drones for ecosystem mapping requires compliance with regulations and guidelines set by aviation authorities. Researchers need to obtain the necessary permits, follow safety protocols, and adhere to privacy laws when conducting aerial surveys.
3. Cost and Accessibility
The cost of acquiring and operating drones, as well as the specialized software and equipment, can be a barrier for some researchers. Additionally, not all ecosystems are easily accessible or suitable for drone surveys, especially in remote or challenging environments.
Future Prospects and Trends
Looking ahead, the future of mapping ecosystems using drones holds great promise. Advances in drone technology, sensors, and artificial intelligence are enhancing the capabilities of aerial surveys and data analysis. Researchers are exploring new applications, such as using drones for autonomous monitoring, predictive modeling, and real-time data visualization.
Furthermore, collaborations between researchers, conservation organizations, and drone manufacturers are driving innovation in ecosystem mapping. By sharing knowledge, expertise, and best practices, the scientific community can harness the full potential of drones to address pressing environmental challenges and inform evidence-based decision-making.
Conclusion
To wrap things up, mapping ecosystems using drones represents a powerful tool for environmental research and conservation. By leveraging the capabilities of drones for aerial surveys, researchers can gather valuable data, monitor ecosystem health, and inform conservation strategies. While there are challenges and considerations to overcome, the benefits of drone mapping far outweigh the limitations. As technology continues to evolve and improve, drones will play an increasingly important role in understanding and protecting our planet’s diverse ecosystems.
Next time you look up at the sky and see a drone buzzing overhead, remember that it’s not just a flying gadgetit’s a valuable tool for mapping the intricate tapestry of life that makes up our ecosystems.